Update: Connections 2050
On September 25, 2025, Update: Connections 2050 was adopted by DVRPC’s Board as Greater Philadelphia's Long-Range Plan. The Plan serves as a blueprint for prioritizing $78 billion in capital transportation investment in the region by 2050. It considers future population growth, economic trends, environmental concerns, and technological advancements to guide investments in roads, public transit, biking, walking infrastructure, and other transportation modes.
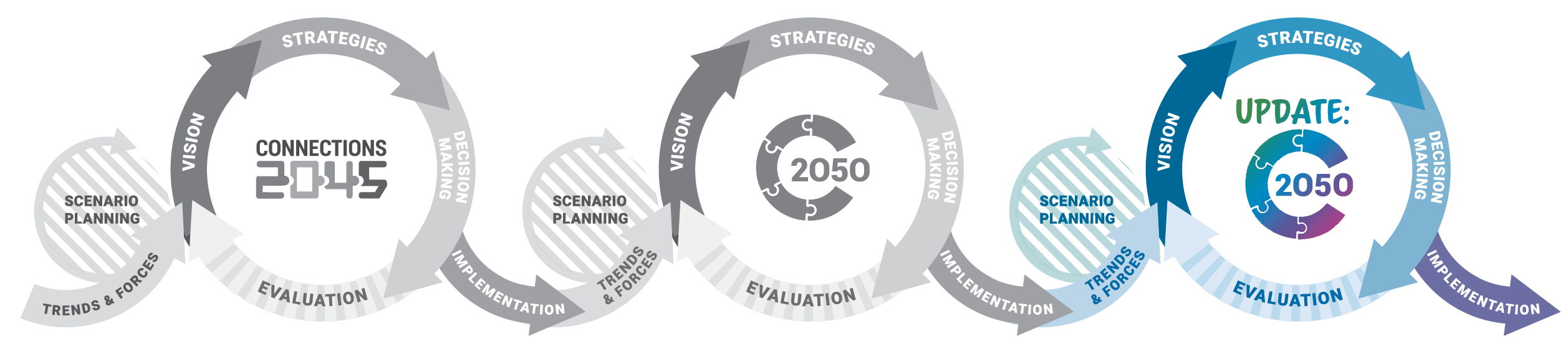
Use the icons or links below to access the Plan and related products.
See what else we’ve been up to:



